Legality of bestiality in the United States: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
The only federal law prohibiting zoophilic pornography, is 18 USC 2256, which prohibits distribution in interstate commerce and on federal property of child pornography of a minor under 18 years old engaging in "sexually explicit conduct" of bestiality. | The only federal law prohibiting zoophilic pornography, is 18 USC 2256, which prohibits distribution in interstate commerce and on federal property of child pornography of a minor under 18 years old engaging in "sexually explicit conduct" of bestiality. | ||
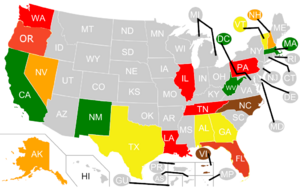
The Constitutional definition of obscenity was narrowed by the US Supreme Court in the 1985 case '''''Brockett v. Spokane Arcades, Inc'''.'', which the court endorsed the Model Penal Code of obscenity. The Model Penal Code prohibition against deviate sexual intercourse includes "sexual intercourse ''per os'' or ''per anum'' between human beings who are not husband and wife, and any form of sexual intercourse with an animal." Federal law does not ban obscenity outright; it leaves this to state and local law. Federal statutes prohibit, among other things, the transmission of obscene matter as defined by state law, in interstate commerce and on federal land. | [[File:Legality of sale and distribution of zoophilic pornography in the United States- .png|thumb|'''GREEN''' Sale and distribution of zoophilic pornography is legal | ||
'''YELLOW''' Sale and distribution of zoophilic pornography is a misdemeanor | |||
'''ORANGE''' Sale and distribution of zoophilic pornography is a misdemeanor or a felony | |||
'''RED''' Sale and distribution of zoophilic pornography is a felony | |||
'''BROWN''' Sale and distribution of zoophilic pornography is illegal; unknown punishment | |||
'''GRAY''' Unknown]]The Constitutional definition of obscenity was narrowed by the US Supreme Court in the 1985 case '''''Brockett v. Spokane Arcades, Inc'''.'', which the court endorsed the Model Penal Code of obscenity. The Model Penal Code prohibition against deviate sexual intercourse includes "sexual intercourse ''per os'' or ''per anum'' between human beings who are not husband and wife, and any form of sexual intercourse with an animal." Federal law does not ban obscenity outright; it leaves this to state and local law. Federal statutes prohibit, among other things, the transmission of obscene matter as defined by state law, in interstate commerce and on federal land. | |||
Private Internet connections in the United States are not subject to censorship imposed by the government. However, private businesses, schools, libraries, and government offices may use filtering software at their discretion, and in such cases courts have ruled the use of such software does not violate the First Amendment. | Private Internet connections in the United States are not subject to censorship imposed by the government. However, private businesses, schools, libraries, and government offices may use filtering software at their discretion, and in such cases courts have ruled the use of such software does not violate the First Amendment. | ||
| Line 58: | Line 68: | ||
Revision as of 19:45, 14 April 2023
Legality of bestiality in the United States looks at the laws prohibiting bestiality in the United States of America. The legality of sex with animals has been steadily decreasing over the past 20 years. As of February 10, 2018, 45 states and 2 territories ban sex with animals, while 5 states and the District of Columbia have decriminalized it (due to repeal of sodomy laws). In 2017, five states (Texas, Kentucky, West Virginia, Vermont and Nevada) introduced legislation to ban bestiality, with Nevada, Vermont, and Texas enacting laws banning it in 2017. New Hampshire and Ohio also banned sex with animals in 2017 (they had 2016 bills which went into effect in 2017).
In late 2017, a bill was introduced in Wisconsin which intends to make sex with animals a felony there. In 2018, five bills were introduced to ban sex with animals: in California (the California bill would make sex with animals a felony), Louisiana (criminalizes promoting or encouraging it), Hawaii, Kentucky, and West Virginia.
Several states, including Oregon, Washington, Tennessee, Illinois, Florida, Alaska and Ohio, criminalize free speech related to sex with animals (such as promoting or encouraging it). These laws have all been recently enacted.
Ohio has the most lenient prison sentences among states with misdemeanor penalties prohibiting bestiality among any state, with a maximum of 90 days in prison and a $750 dollar fine. Michigan has the most lenient prison sentences among states with minimum felony penalties prohibiting bestiality among any state, with a minimum of 1 day in prison. Maryland has the harshest maximum prison sentences among states with misdemeanor penalties prohibiting bestiality among any state, with a maximum of 10 years in prison and/or a maximum of a $1,000 dollar fine. Rhode Island has the harshest minimum prison sentence among states with felony penalties prohibiting bestiality, with a minimum of 7 years in prison. Idaho and Michigan both have the harshest maximum prison sentences among states with felony penalties prohibiting bestiality among any state, with a maximum of life in prison.
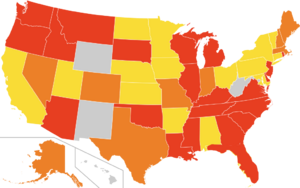
Legality of bestiality in the United States of America
Federal Law
Laws against bestiality in the United States are largely a matter of state rather than federal jurisdiction, except for laws governing the District of Columbia and the U.S. Armed Forces. There is no federal law which explicitly prohibits sex between humans and animals.
The only federal law prohibiting zoophilic pornography, is 18 USC 2256, which prohibits distribution in interstate commerce and on federal property of child pornography of a minor under 18 years old engaging in "sexually explicit conduct" of bestiality.
The Constitutional definition of obscenity was narrowed by the US Supreme Court in the 1985 case Brockett v. Spokane Arcades, Inc., which the court endorsed the Model Penal Code of obscenity. The Model Penal Code prohibition against deviate sexual intercourse includes "sexual intercourse per os or per anum between human beings who are not husband and wife, and any form of sexual intercourse with an animal." Federal law does not ban obscenity outright; it leaves this to state and local law. Federal statutes prohibit, among other things, the transmission of obscene matter as defined by state law, in interstate commerce and on federal land.
Private Internet connections in the United States are not subject to censorship imposed by the government. However, private businesses, schools, libraries, and government offices may use filtering software at their discretion, and in such cases courts have ruled the use of such software does not violate the First Amendment.
District of Columbia
- In 1801, Congress enacted the District of Columbia Organic Act of 1801 that continued all criminal laws of Maryland and Virginia in the now formally structured District, with those of Maryland applying to that portion of the District ceded from Maryland, and those of Virginia applying to that portion ceded from Virginia. At the time, Maryland had a sodomy law applicable only to free males with a punishment of "labor for any time, in their discretion, not exceeding seven years for the same crime, on the public roads of the said county, or in making, repairing or cleaning the streets or bason [sic] of Baltimore-town" and the death penalty for slaves committing sodomy, while Virginia had a penalty of 1–10 years for free persons committing sodomy, but had the death penalty for slaves committing sodomy. The law went into effect on February 27, 1801.
- In 1831, Congress established penalties in the District of Columbia for a number of crimes, but not for sodomy. It specified that "every other felony, misdemeanor, or offence not provided for by this act, may and shall be punished as heretofore[.]" At the time, Maryland and Virginia had a penalty of 1–10 years for committing sodomy. It went into effect on March 2, 1831.
- In 1892, Congress passed a law for the District of Columbia that states that "for the preservation of the public peace and the protection of property within the District of Columbia." Labeled in the law as vagrants were "all public prostitutes, and all such persons who lead a notoriously lewd or lascivious course of life[.]" All offenders had to post bond of up to $200 for good behavior for a period of six months. The law went into effect on July 29, 1892.
- In 1898, Congress deleted the word "notoriously" from the provision concerning a lewd or lascivious course of life, thereby allowing prosecution of those without notoriety. The bond for good behavior was raised to $500, and the law was made clearly gender-neutral. The law went into effect on July 8, 1898.
- In 1901, Congress adopting a new code for the District of Columbia that expressly recognized common-law crimes, with a penalty for them of up to five years and/or a $1,000 fine. The law went into effect on March 3, 1901.
- In 1935, Congress passed a law for the District of Columbia that made it a crime for "any person to invite, entice, persuade, or to address for the purpose of inviting, enticing, or persuading any person or persons...to accompany, to go with, to follow him or her to his or her residence, or to any other house or building, inclosure, or other place, for the purpose of prostitution, or any other immoral or lewd purpose." It imposed a fine of up to $100, up to 90 days in jail, and courts were permitted to "impose conditions" on anyone convicted under this law, including "medical and mental examination, diagnosis and treatment by proper public health and welfare authorities, and such other terms and conditions as the court may deem best for the protection of the community and the punishment, control, and rehabilitation of the defendant." The law went into effect on August 14, 1935.
- In 1948, Congress enacted the first sodomy law in the District of Columbia, which established a penalty of up to 10 years in prison or a fine of up to $1,000 for sodomy. Also included with this sodomy law was a psychopathic offender law and a law "to provide for the treatment of sexual psychopaths in the District of Columbia, and for other purposes." The law went into effect on June 9, 1948.
- In 1981, after the District of Columbia regained home rule from Congress, it enacted a law that repealed the sodomy law, as well as other consensual acts, and made the sexual assault laws gender-neutral. However, the U.S. House exercised the power that it retained to veto laws passed by the District of Columbia Council. On October 1, 1981, the House voted 281-119 to disallow the new law. In 1983, one of the House vetoes by Congress were declared unconstitutional by the U.S. Supreme Court in the case of Immigration and Naturalization Service v. Chadha, but the law was repealed by an act of Congress in a revision to the home-rule law required by the Supreme Court decision.
United States Armed Forces
On March 1, 1917, the Articles of War of 1916 are implemented. This included a revision of the Articles of War of 1806, the new regulations detail statutes governing U.S. military discipline and justice. Under the category Miscellaneous Crimes and Offences, Article 93 states that any person subject to military law who commits "assault with intent to commit sodomy" shall be punished as a court-martial may direct. On June 4, 1920, Congress modified Article 93 of the Articles of War of 1916. It was changed to make the act of sodomy itself a crime, separate from the offense of assault with intent to commit sodomy. It went into effect on February 4, 1921.
On May 5, 1950, the UCMJ was passed by Congress and was signed into law by President Harry S. Truman, and became effective on May 31, 1951. Article 125 forbids sodomy among all military personnel, defining it as "any person subject to this chapter who engages in unnatural carnal copulation with another person of the same or opposite sex or with an animal is guilty of sodomy. Penetration, however slight, is sufficient to complete the offence."
On December 1, 2011, the US Senate voted 93-7 in favor of the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2012, which contained in it a provision repealing Article 125 of the UCMJ. The bill died in Congress.
On December 26, 2013, President Barack Obama signed the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2014 into law. The law repealed the ban on consensual sodomy found in Article 125 and added a specific provision in Article 125 of the UCMJ that specifically bans bestiality:
(b) Bestiality.— Any person subject to this chapter who engages in unnatural carnal copulation with an animal is guilty of bestiality and shall be punished as a court-martial may direct. (c) Scope of Offenses.— Penetration, however slight, is sufficient to complete an offense under subsection (a) or (b). —
On September 16, 2016, President Barack Obama signed Executive Order 13740, which included a new provision under the UCMJ to apply anywhere on Earth where the United States Armed Forces military is stationed and will be on a par with states’ animal cruelty statutes. Violations will be separated by “abuse, neglect, or abandonment of an animal” and “bestiality.”
Current status
Current status
tete etet etet
gggg gggg
| Federal government, federal district, or state | Bestiality | Sale and distribution of zoophilic pornography | Ownership of zoophilic pornography |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Legal
Illegal for armed service members since February 4, 1921 Penalty: Dishonorable discharge, forfeiture of all pay and allowances, and confinement for 5 years. |
N/A | N/A |
| Alabama | Illegal since July 1, 2014
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison and/or a maximum of a $6,000 dollar fine |
Illegal since July 1, 2014
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison and/or a maximum of a $6,000 dollar fine<a href="#cite_note-Section_13A-6-221-40">[38]</a><a href="#cite_note-Section_13A-6-220-41">[39]</a><a href="#cite_note-Alabama_Misdemeanor_Crimes_by_Class_and_Sentences-42">[40]</a> |
|
| Alaska | Illegal since September 13, 2010
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison; additionally a court may require forfeiture of any animal affected to the state or to a custodian that supplies shelter, care, or medical treatment for the animal, require the defendant to reimburse the state or a custodian for all reasonable costs incurred in providing necessary shelter, care, veterinary attention, or medical treatment for any animal affected, or prohibit or limit the defendant's ownership, possession, or custody of animals for up to 10 years, or all of the above (first offense) |
Illegal since September 13, 2010
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison; additionally a court may require forfeiture of any animal affected to the state or to a custodian that supplies shelter, care, or medical treatment for the animal, or require the defendant to reimburse the state or a custodian for all reasonable costs incurred in providing necessary shelter, care, veterinary attention, or medical treatment for any animal affected, or prohibit or limit the defendant's ownership, possession, or custody of animals for up to 10 years, or all of the above (first offense) |
|
| Arizona | Illegal since September 21, 2006
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison and/or a maximum of a $15,000 dollar fine; additionally a court may require undergoing a psychological assessment and participate in appropriate counseling at the convicted person's own expense, or reimburse an animal shelter for reasonable costs incurred for the care and maintenance of any animal that was taken to the animal shelter as a result of conduct proscribed by subsection A of this section, or all of the above (presumptive term) |
Illegal
Penalty: Maximum of 2 years in prison and/or a maximum of a $15,000 dollar fine (presumptive term) |
|
| Arkansas | Illegal since March 2, 1819
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison and a maximum of a $2,500 dollar fine |
Illegal
Penalty: Maximum of 90 days in prison and a maximum of a $1,000 dollar fine (publicly displaying obscene material for advertising purposes if, for advertising purposes, he or she knowingly displays publicly or causes to be displayed publicly obscene material or permits any display of obscene material on premises owned, rented, or operated by him or her) |
|
| California | Illegal
Penalty: Maximum of 6 months in prison and/or a maximum of a $5,000 dollar fine |
Legal | |
| Colorado | Illegal since July 1, 2007
Penalty: Minimum of 6 months in prison to a maximum of 1 and a half years in prison and/or a minimum of a $500 dollar fine to a maximum of a $5,000 dollar fine; additionally a court may order an evaluation, which requires the convicted to pay the cost of the evaluation, unless the person qualifies for a public defender, to be conducted prior to sentencing to assist the court in determining an appropriate sentence and if the evaluation results in a recommendation of treatment and if the court so finds, the person shall be ordered to complete an anger management treatment program or any other treatment program that the court may deem appropriate.< |
Illegal
Penalty: Minimum of 6 months in prison to a maximum of 1 and a half years in prison and/or a minimum of a $500 dollar fine to a maximum of a $5,000 dollar fine (promotes or possesses with intent to wholesale promote any obscene material) |
|
| Connecticut | Illegal
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison and a maximum of a $2,000 dollar fine |
Legal | |
| Delaware | Illegal since July 6, 1993
Penalty: Maximum of 8 years in prison |
Legal | |
| District of Columbia | Legal since May 23, 1995 | Legal | |
| >Florida | Illegal since October 1, 2011
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison and a $1,000 dollar fine |
Illegalsince October 1, 2011
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison and a $1,000 dollar fine |
|
| Georgia | Illegal since June 1, 1834
Penalty: Maximum of 5 years in prison |
Illegal
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison and a maximum of a $5,000 dollar fine |
|
| Hawaii | Legal | Legal | |
| Idaho | Illegalsince April 1, 1972
Penalty: Minimum of 5 years in prison to a maximum of life in prison |
Legal | |
| Illinois | Illegal since January 1, 2003
Penalty: Maximum of 3 years in prison and a $25,000 dollar fine; additionally a court may order the defendant not to harbor animals or reside in any household where animals are present for a reasonable period of time or permanently, relinquish and permanently forfeit all animals residing in the household to a recognized or duly organized animal shelter or humane society, undergo a psychological evaluation and counseling at defendant's expense, reimburse the animal shelter or humane society for any reasonable costs incurred for the care and maintenance of the animal involved in the sexual conduct or sexual contact in addition to any animals relinquished to the animal shelter or humane society, order the seizure of all animals involved in the alleged violation as a condition of bond of a person charged with a violation of this Section, or all of the above |
Illegal since January 1, 2003
Penalty: Maximum of 3 years in prison and a $25,000 dollar fine; additionally a court may order the defendant not to harbor animals or reside in any household where animals are present for a reasonable period of time or permanently, relinquish and permanently forfeit all animals residing in the household to a recognized or duly organized animal shelter or humane society, undergo a psychological evaluation and counseling at defendant's expense, reimburse the animal shelter or humane society for any reasonable costs incurred for the care and maintenance of the animal involved in the sexual conduct or sexual contact in addition to any animals relinquished to the animal shelter or humane society, order the seizure of all animals involved in the alleged violation as a condition of bond of a person charged with a violation of this Section, or all of the above |
|
| Indiana | Illegal since July 1, 2007
Penalty: Minimum of 6 months to a maximum of 2 and a half years in prison and a minimum of a $5,000 dollar fine to a maximum of a $10,000 dollar fine |
> Legal | |
| Iowa | Illegal since May 16, 2001
Penalty: Maximum of 2 years in prison and a minimum of a $625 dollar fine to a maximum of a $6,250 dollar fine; additionally the court shall require the person to submit to a psychological evaluation and treatment at the person’s expense. |
Illegal
Penalty: Maximum of 2 years in prison and a minimum of a $625 dollar fine to a maximum of a $6,250 dollar fine |
|
| Kansas | Illegal since 1850s
Penalty: Maximum of 6 months in prison and a maximum of a $1,000 dollar fine |
Unknown | |
| Kentucky | Illegal since June 27, 2019
Penalty: Maximum of 5 years in prison, a maximum of a $10,000 dollar fine, relinquish custody of all animals under the person's control, unless the person convicted of violating this section is not the owner of the animal that was the subject of the violation, then the animal shall be returned to the owner of the animal, an animal returned to an owner under this section shall not be spayed or neutered prior to being returned, not harbor, own, possess, or exercise control over any animal, reside in any household where animals are present, or work or volunteer in a place where the person has unsupervised access to animals for a minimum of five years after completion of the imposed sentence, attend an appropriate treatment program or obtain psychiatric or psychological counseling, at the person's expense, and reimburse the agency caring for the animal for reasonable costs incurred for the care and treatment of the animal from the date of impoundment until the disposition of the criminal proceeding. |
Illegal since June 27, 2019
Penalty: Maximum of 5 years in prison, a maximum of a $10,000 dollar fine, relinquish custody of all animals under the person's control, unless the person convicted of violating this section is not the owner of the animal that was the subject of the violation, then the animal shall be returned to the owner of the animal, an animal returned to an owner under this section shall not be spayed or neutered prior to being returned, not harbor, own, possess, or exercise control over any animal, reside in any household where animals are present, or work or volunteer in a place where the person has unsupervised access to animals for a minimum of five years after completion of the imposed sentence, attend an appropriate treatment program or obtain psychiatric or psychological counseling, at the person's expense, and reimburse the agency caring for the animal for reasonable costs incurred for the care and treatment of the animal from the date of impoundment until the disposition of the criminal proceeding |
|
| Louisiana | Illegal
Penalty: Maximum of 5 years in prison and/or a maximum of a $2,000 dollar; additionally a court may relinquish custody of all animals, prohibited from owning or processing any animal for a period of time as deemed appropriate by the court, but not less than five years, not reside in any household where an animal is present, undergo a psychological evaluation for sex offenders and participate in any recommended psychological treatment, reimburse the owner of the animal for expenses incurred for medical treatment or rehabilitation of the victimized animal if the convicted person is not the owner of the animal, required to participate in a sex offender program, law enforcement officer investigating a violation of this Section may lawfully take possession of an animal that he has reason to believe has been victimized under this Section in order to protect the health or safety of the animal or the health or safety of others, and to obtain evidence of the offense, or all of the above (first offense) |
Illegal since May 25, 2018
Penalty: Maximum of 5 years in prison and/or a maximum of a $2,000 dollar; additionally a court may relinquish custody of all animals, prohibited from owning or processing any animal for a period of time as deemed appropriate by the court, but not less than five years, not reside in any household where an animal is present, undergo a psychological evaluation for sex offenders and participate in any recommended psychological treatment, reimburse the owner of the animal for expenses incurred for medical treatment or rehabilitation of the victimized animal if the convicted person is not the owner of the animal, required to participate in a sex offender program, law enforcement officer investigating a violation of this Section may lawfully take possession of an animal that he has reason to believe has been victimized under this Section in order to protect the health or safety of the animal or the health or safety of others, and to obtain evidence of the offense, or all of the above (first offense) |
|
| Maine | Illegalsince September 21, 2001
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison and a maximum of a $2,000 dollar fine |
Unknown | |
| Maryland | Illegal since June 20, 1632
Penalty: Maximum of 10 years in prison and/or a maximum of a $1,000 fine |
Unknown | |
| Massachusetts | since November 15, 1636 as part of the <a href="/web/20200910091758/https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plymouth_Colony" title="Plymouth Colony">Plymouth Colony Illegal since November 1641 as part of the <Massachusetts Bay Colony Penalty: Maximum of 20 years in prison |
Legal | |
| Michigan | Illegal since November 4, 1816
Penalty: Maximum of 15 years in prison |
Unknown | |
| Minnesota | Illegalsince March 3, 1849
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison and $3,000 fine |
Unknown | |
| Mississippi | Illegal since June 1802
Penalty: Maximum of 10 years in prison |
Unknown | |
| Missouri | Illegal since August 28, 2002
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison and $1,000 fine< |
Unknown | |
| Montana | Illegal since January 1865
Penalty: Maximum of 10 years in prison and a $50,000 fine |
Unknown | |
| Nebraska | Illegal since March 16, 1855
Penalty: Maximum of 3 months in prison and $500 fine |
> Unknown | |
| Nevada | Illegal since October 1, 2017
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison, a $2,000 dollar fine, or both< |
Illegal since October 1, 2017
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison, a $2,000 dollar fine, or both< |
|
| New Hampshire | > Illegal since January 1, 2017
Penalty: Maximum of 12 months in prison, a $2,000 fine, and goes on the New Hampshire <a href="/web/20200910091758/https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sex_offender_registry" title="Sex offender registry">sex offender registry</a> (first offense) |
Illegal
Penalty: Maximum of 12 months in prison, a $2,000 fine, and goes on the New Hampshire sex offender registry (first offense) |
|
| New Jersey | > Illegal since November 9, 2015
Penalty: Maximum of 18 months imprisonment, fine up to $10,000, or both> |
Unknown | |
| New Mexico | Legal< | Legal | |
| New York | Illegal since the 1600s
Penalty:
|
Unknown | |
| North Carolina | Illegal since the time from November 17, 1715 to January 19, 1716
Penalty: Minimum of 3 months in prison to a maximum of 1 year in prison< |
Illegal
Penalty: Unknown< |
|
| North Dakota | Illegal since April 28, 1862
Penalty: Maximum of one year in prison and $2,000 fine> |
> Unknown | |
| Ohio | Illegal statewide since March 19, 2017
Penalty: Maximum of up to 90 days in prison and $750 dollar fine <a > Illegal in <a href="/web/20200910091758/https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Warren,_Ohio" title="Warren, Ohio">Warren, Ohio</a> since June 22, 2016 Penalty: Maximum of up to 180 days in prison and $1,000 dollar fine |
Unknown | |
| Oklahoma | Illegal since May 2, 1890
Penalty: Maximum of 10 years in prison< |
Unknown | |
| Oregon | Illegal since 2001
Penalty:
|
............................
Penalty: Maximum of one 1 year in prison and a $6,250 fine> |
Illegal since January 1, 2016
Penalty: Maximum of one 1 year in prison and a $6,250 fine |
| Pennsylvania | Illegal
Penalty: Maximum of 2 years in prison and a $5,000 fine< |
tetsetestsetestet
Penalty: Maximum of seven years in prison and up to $15,000 fine. |
|
| Rhode Island | > Illegal since May 1647
Penalty: Maximum of 20 years in prison |
Unknown | |
| South Carolina | Illegal since December 12, 1712
Penalty: Maximum of 5 years in prison and a $500 fine |
Unknown | |
| South Dakota | Illegal since 2003
Penalty: Maximum of 2 years in prison and a $4,000 fine |
Unknown | |
| Tennessee | Illegal since 2007
Penalty: Maximum of 6 years in prison and a $3,000 fine |
Illegal since 2007
Penalty: Maximum of 6 years in prison and a $3,000 fine |
|
| Texas | Illegal statewide since September 1, 2017 >Lubbock, Texas</a> Penalty: Maximum of 2 years in prison |
Illegal
Penalty: Maximum of a 1 year in prison and/or a fine of not more than $4,000 |
|
| Utah | Illegal since May 3, 1993
Penalty: Maximum of 6 months in prison and a $1,000 fine |
Unknown | |
| Vermont | Illegal since July 1, 2017
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison, $2,000 fine, or both |
Illegal since July 1, 2017
Penalty: Maximum of 1 year in prison, $2,000 fine, or both |
|
| Virginia | Illegal since March 23, 1661
Penalty: Maximum of 5 years in prison and a $2,500 fine |
Unknown | |
| Washington | Illegal since June 7, 2006
Penalty: Maximum of 5 years in prison and a $10,000 fine |
Illegal since June 7, 2006
Penalty: Maximum of 5 years in prison and a $10,000 fine |
|
| West Virginia | Legal;<a href="#cite_note-Rawstory-95">[81]</a><a href="#cite_note-241">[206]</a> 2017 bill<a href="#cite_note-WV1-4">[4]</a> & 2018 bill<a href="#cite_note-WV2018-11">[11]</a> would've banned it | Legal | |
| Wisconsin | Illegal since July 3, 1836; 2017/2018 bill would make it a felony<a Penalty: Maximum of 9 months in prison and a $10,000 fine $10,000; for a repeat offender, maximum of two years in prison<a href="#cite_note-244">[209]</a> |
Unknown | |
| Wyoming | Legal | Unknown |